Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the leg. Because a clot can travel to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism, get evaluated quickly. A duplex ultrasound is the first test to quickly and comfortably confirm or rule out DVT.
A DVT is a blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the calf or thigh, sometimes in the pelvis, and less often in an arm. Leg symptoms are swelling on one side, pain or tenderness of the calf, warmth, and redness or color change. If you also have chest pain, sudden shortness of breath, or cough up blood, call 911; these are warning signs of a pulmonary embolism.

What Is DVT?
What causes DVT?
Clots are more likely to form when the blood flow slows down or the clotting tendency is increased. There are a number of risk factors, including recent surgery or hospitalization, immobility or extended travel, pregnancy, estrogen-replacement therapy, active malignancy, prior DVT/PE, obesity, cigarette smoking, and age. There is also the option of employing a clinical scoring system (e.g, Wells criteria) for pre-test probability assessment and next step determination, including ultrasound and D-dimer testing.
DVT Symptoms: When to get care
- New one-sided leg swelling
- Calf pain or tenderness, warmth, or redness
- A leg that feels heavier or larger than the other
Call the same day if these are new for you. If you also have chest pain, shortness of breath, fainting, or coughing up blood, call 911.

We perform a test known as duplex ultrasound, a special non-surgical scan that photographs your veins, blood flow, and obstruction due to a clot. Depending on your history and physical examination, your clinician might also arrange a different blood test known as D-dimer to rule out DVT when the suspicion is low.
Treatment of DVT: What’s Next?
If there is DVT, therapy usually starts with anticoagulation, or blood thinners, for approximately 3 months. Duration depends on the location of the clot, why it developed, and your risk of bleeding. For an isolated calf-vein DVT that is small, careful follow-up using ultrasound may be utilized if the clot is not extending. Your imaging and your clinical course determine the treatment plan.
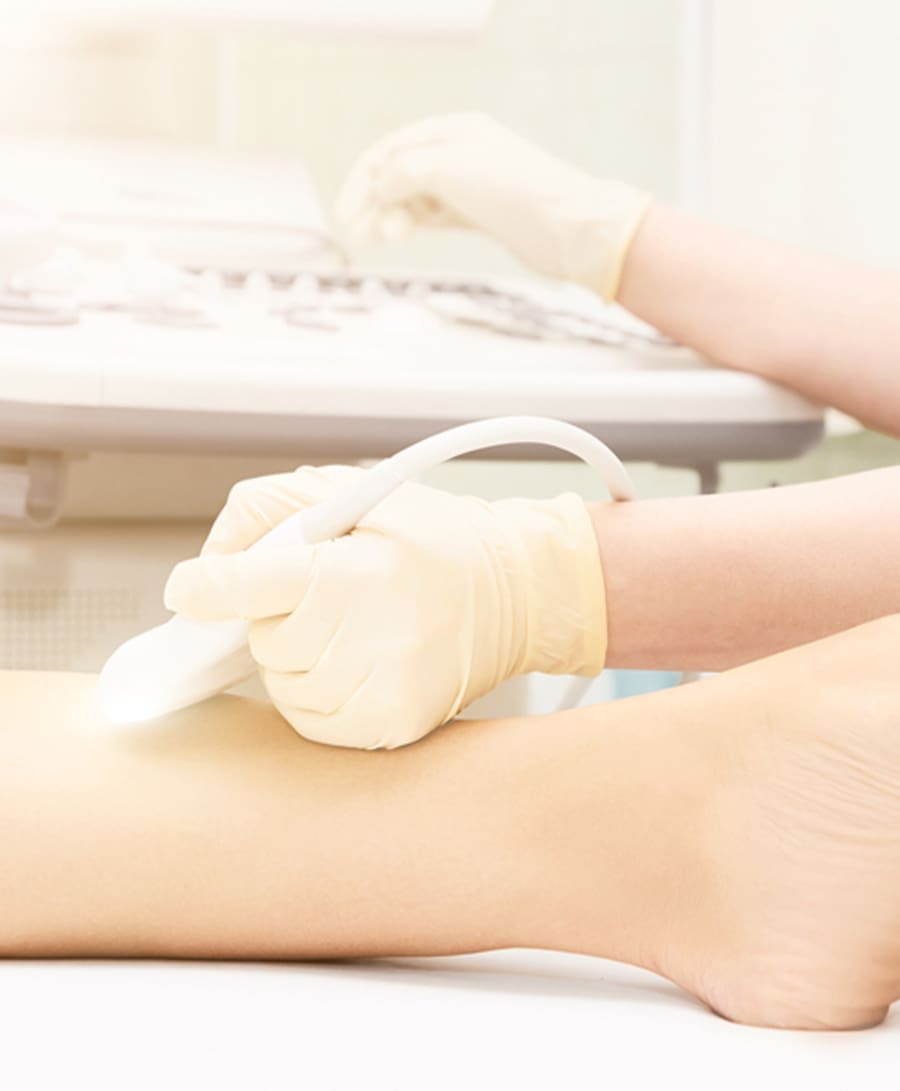
How Is DVT Diagnosed?

Same-Day DVT Ultrasound
We offer same-day appointments for urgent leg ultrasounds, with results sent to your doctor on the same day. If the study is positive, we will coordinate with your doctor or the ER so your treatment is not delayed. Insurance is usually covered when it is medically necessary.
Get Checked Today, Same-Day DVT Ultrasound
Call the DVT Specialists at Vein Institute: (203) 426-5554
New calf swelling, pain, warmth, or redness? Contact us at Vein Institute, and we’ll schedule a same-day duplex ultrasound and send results to your doctor within an hour of the study. Most insurance is accepted when medically necessary.
